Announcement from Japan Customs - Mandatory to Use ACP in Many Cases - Attorney for Customs Procedures
We would like to inform you about a significant revision by Japan Customs, which clarifies the definition of an Importer. This change took effect on October 1, 2023.
With the revision, there has been an increase in cases where foreign corporations must use an Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) to become an Importer of Record (IOR) themselves. It is no longer feasible to nominate another entity merely in name as the importer.
In instances other than normal import transactions between an overseas seller and a Japanese buyer, where the importer does not have the authority to dispose of the goods after importation (for example, when a foreign corporation does not become the IOR themselves and nominates a forwarder, customs broker, or another third party who is not involved in the transaction to be the nominal IOR), there is a high probability that approval will not be granted as such nominations are not recognized as legitimate importers, therefore careful attention is required.
As a professional ACP firm, we follow the law to facilitate proper import procedures. You can entrust us with your importation needs with confidence. We look forward to discussing further with you.
Japan Customs' Official Guideline for E-Commerce Sellers
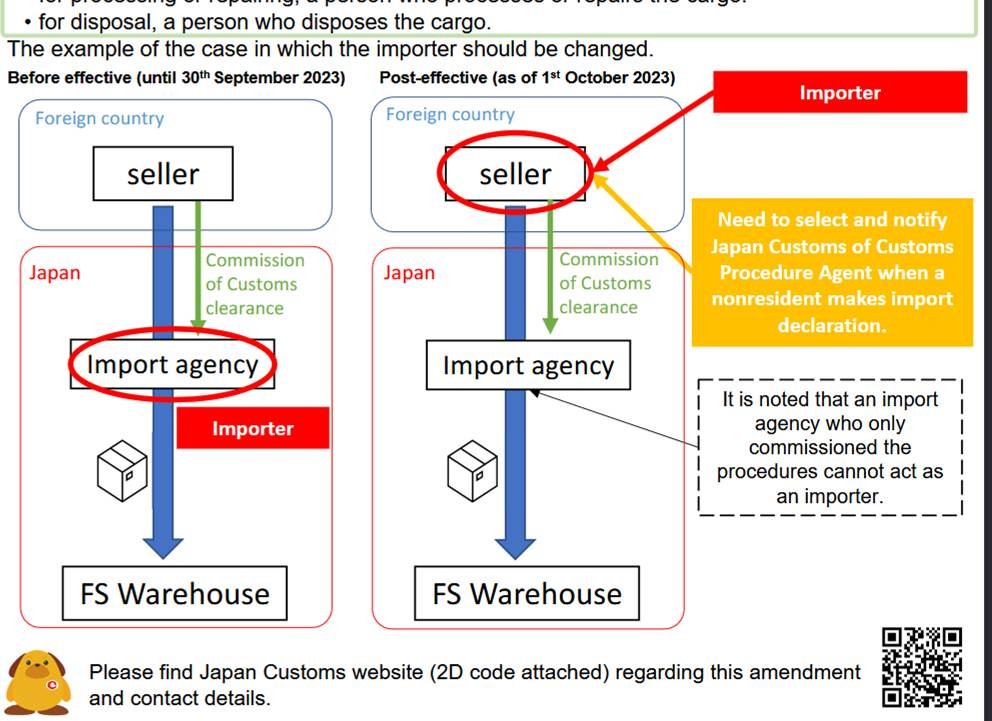
Here is the official guideline from Japan Customs. On page 2 of the leaflet, you'll see a clear comparison:
- On the left side, which reflects the rule before September 30, 2023, it was allowed for an "Import Agency" (such as a logistics or warehouse company) to act as the Importer of Record (IOR).
- On the right side, from October 2023 onward, the Seller must be the IOR by appointing a Customs Procedures Agent — which is what we refer to as an ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedures).
- Japan Customs: Revision of Import Declaration Items and Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP) System
- Japan Customs Notice - Available in English, Chinese, Korean, and Japanese
Revisions Effective October 1, 2023:
Definition of the Importer
- Regarding a cargo imported under an import transaction, an importer is equivalent to “a person who imports a cargo” defined in Article 6-1 (1), General Notification of the Customs Act. ….. This means, the Consignee, etc., in the case of imports conducted through normal transactions between an overseas seller and a Japanese buyer
- In the cases other than above, an importer is a Person Having the Right of Disposal of the import cargo at the time of import declaration. If there is another person who acts on the purpose of the import*, that person is also included:
In case of a cargo imported:
- under lease contracts, a person who rents and uses the cargo.
- for consignment sales, a person who sells the cargo in the name of himself/herself (consignee) by accepting the commission.
- for processing or repairing, a person who processes or repairs the cargo.
- for disposal, a person who disposes the cargo.
Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
Recommended Content

Case Study: Directives to use ACP
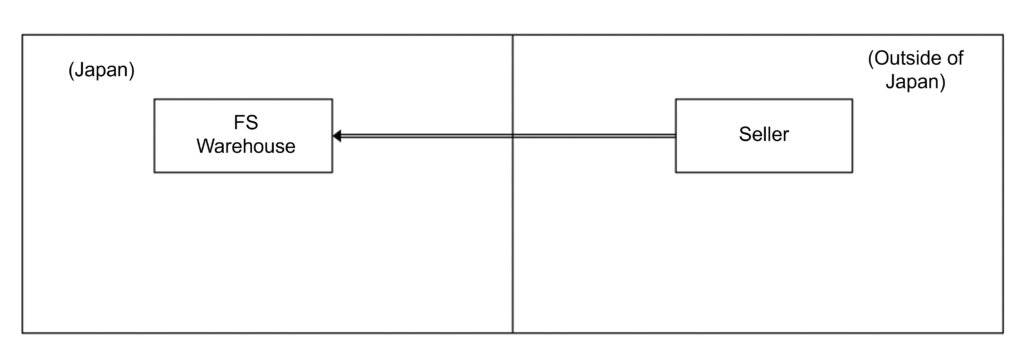
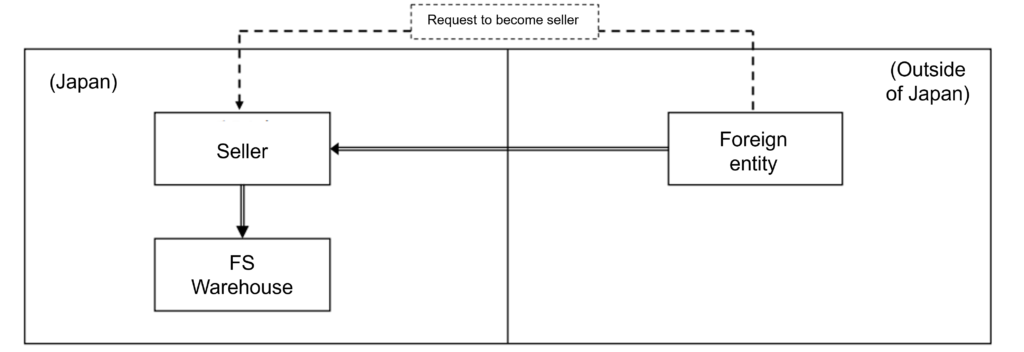
Case 1: Importing Goods Using FS (Fulfillment Services) by Non-resident Sellers
A non-resident seller plans to import goods for sale domestically using FS provided by EC platform operators. At the time of import declaration, there is no sales contract between the seller and the consumer. The seller (non-resident) is the main entity for sales on the EC platform after domestic pickup of the goods. Therefore, the seller, who aims to sell the goods in accordance with the purpose of import, needs to become the import declarant and appoint Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP) to carry out the import declaration.
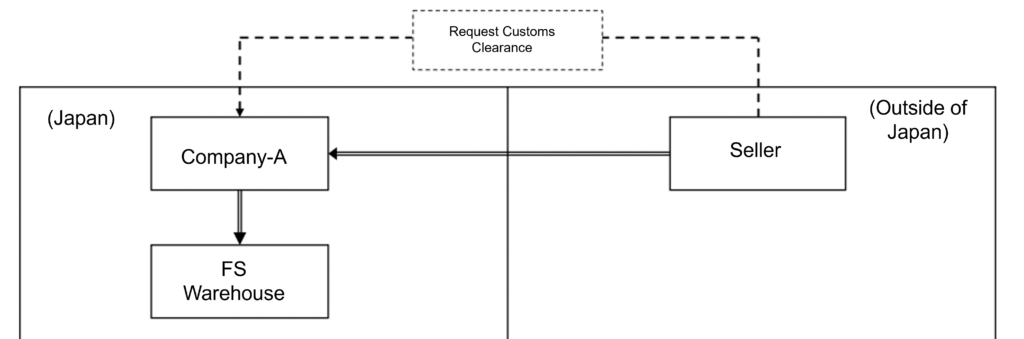
Case 2: Importing Goods Using FS by Non-resident Sellers
A non-resident seller plans to import goods for sale domestically using FS provided by EC platform operators. At the time of import declaration, there is no sales contract between the seller and the consumer. The seller (non-resident) entrusts domestic customs clearance arrangements to Company-A (located in Japan), but the main entity for selling the goods within the domestic market using FS remains the seller (non-resident). It is planned that the seller (non-resident), who intends to sell the goods on the EC platform after domestic pickup, should become the import declarant and appoints Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP) in accordance with the purpose of import declaration.
Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
Recommended Content

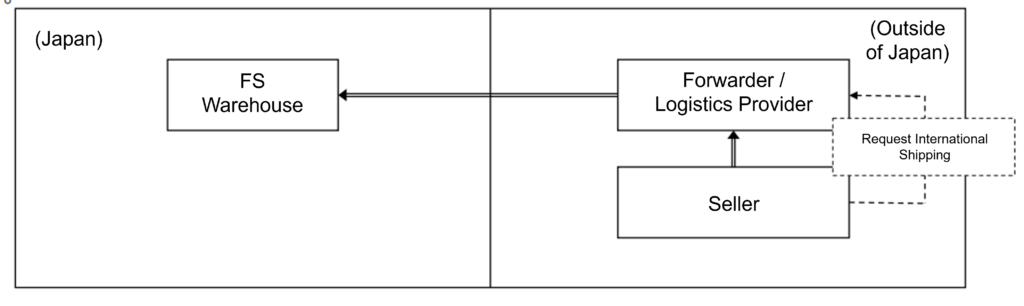
Case 3: Importing Goods Using FS by Non-resident Sellers
A non-resident seller plans to import goods for sale domestically using FS provided by EC platform operators. At the time of import declaration, there is no sales contract between the seller and the consumer. The seller (non-resident) entrusts the transportation of the goods from overseas sellers to Japan to an overseas forwarder, but the main entity for selling the goods within the domestic market using FS remains the seller (non-resident). It is planned that the seller (non-resident), who intends to sell the goods on the EC platform after domestic pickup, will become the import declarant and appoints Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP) in accordance with the purpose of import declaration.
Case 4: Importing Goods for Consignment Sales
Goods (consignment sales goods) intended for domestic sale by an assignee who has received consignment sales from a non-resident consignor are imported. The imported goods are stored in an FS warehouse and sold on the EC platform under the name of the assignee. The assignee is the main entity for selling the goods within the domestic market using FS.
Either of the following options is necessary:
The consignor (non-resident) who has the authority to dispose of the consignment sales goods becomes the import declarant, appoints Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP), and carries out the import declaration.
The assignee (i.e., the seller on the EC platform) who conducts the act of selling on behalf of themselves as the purpose of import becomes the import declarant and carries out the import declaration.
Recommended Content

Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
For more information regarding the revised regulations by the Japan Customs, please refer to the following:
(Link: Revision of Import Declaration Items and Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP) System) Ministry of Finance, Japan Customs July 2023 With the expansion of cross-border e-commerce, the importation of goods for online shopping has increased, leading to a significant number of cases involving the smuggling of illegal drugs and counterfeit goods that infringe upon intellectual property rights. Particularly concerning are instances of tax evasion, where goods imported through fulfillment services (FS) are declared at unreasonably low prices to evade customs duties.
In light of these circumstances, we have conducted a review of the existing system to ensure the continued facilitation of smooth imports while effectively combating smuggling activities and ensuring proper taxation. Effective from October 1, (2023), there will be an addition to the import declaration items under the Customs Law Enforcement Order, requiring the inclusion of the "address and name of the person intending to import the goods" at the time of import declaration.
Furthermore, there will be additions to the declaration items for Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP), including information regarding the relationship between the declarant and the Attorney for Customs Procedure (ACP). Additionally, it will be mandatory to submit the contractual documents between the declarant and the ACP. For specific details regarding the revisions to the system, please refer to the following reference materials.
Reference (Japan Customs)
Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
Recommended Content

Please Be Aware
- In cases where foreign corporations (non-residents) without an office in Japan import or export goods, failure to properly prepare an Importer of Record (IOR) or Exporter of Record (EOR) through an Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) or similar means can result in goods being held at customs, leading to significant delays and costs. To avoid such risks, please make thorough preparations.
- If an ACP is needed, it is crucial to utilize the services of an experienced ACP well-versed in customs-related laws and regulations. The import and export operations of non-residents/foreign corporations using an ACP are treated as unique cases. Many customs brokers are not familiar with these procedures, leading to incidents where goods are detained for extended periods due to unsuccessful explanations to customs. (Customs will not permit the import if the explanations provided by the importer or customs broker are unsatisfactory, resulting in the goods being detained until customs is convinced.)
- We highly recommend utilizing our services as professional experts in customs, knowledgeable about customs-related laws and regulations. With a proven track record of resolving numerous issues through direct consultations with customs officers and customs brokers, our clients supported as an ACP now exceed 200 companies. We are committed to delivering industry-leading results with our expertise.
Why choose us?
We specialize in navigating complex issues at the intersection of customs procedures and taxation—an area where our ability to offer practical, comprehensive support from both perspectives sets us apart. Understanding the close relationship between customs duties and national taxes (especially, Japan Consumption Tax - JCT), and addressing both in an integrated manner, is crucial in the context of international trade.
- Customs and International Trade Professionals - Led by our CEO, Mr. Sawada—Certified Customs Specialist and former KPMG professional—SK Advisory provides expert-level support in Customs and international trade. Mr. Sawada also serves as an external expert for the World Bank’s B-READY project in the field of customs and international trade.
- Full Compliance with Japanese Customs Law - We ensure full adherence to Japanese Customs Law, including Importer of Record (IOR) structure, HS code classification, and customs valuation. We assist in preparing all essential shipping documents for non-resident entities.
- One-Stop Support for ACP and JCT Tax Representative Services - In collaboration with trusted partner tax accountants, we provide comprehensive support for both customs procedures through the Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) and Japan Consumption Tax (JCT) filings through the JCT Tax Representative.
- Multilingual Communication - Our team communicates fluently in English, Japanese, and Chinese, offering smooth coordination with global clients and authorities in Japan.
- Support for Regulated Products - Our ACP/IOR partnership system can manage regulated items, including cosmetics, PSE-products, foodstuffs, and tableware.
- Trusted by Global Clients - Serving around 100 ACP clients annually, including many Amazon sellers, we’re a certified provider on Amazon SPN (Service Provider Network) under Trade Compliance.

Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
Track Record – Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) Services
We have supported import and export operations in Japan for over 200 clients across more than 40 countries.
Examples of International Logistics Partners We Have Worked With
We have a proven track record of working with a wide range of logistics providers. As the Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP), we handle customs-related responsibilities while logistics companies manage transportation and warehousing operations.
- American Overseas Transport (AOT)
- Apex International
- Brink's
- CEVA Logistics
- Coshipper
- Crane Worldwide Logistics
- DB Schenker
- DGX (Dependable Global Express)
- DHL Express
- DHL Global Forwarding
- Dimerco
- DSV Air & Sea
- Expeditors
- FedEx Express
- FERCAM
- GOTO KAISOTEN Ltd.
- Harumigumi
- Herport
- ICL Logistics
- JAS Forwarding
- Kintetsu Express
- Kokusai Express
- Kuehne + Nagel
- Mitsubishi Logistics
- MOL Logistics
- Nankai Express
- Nippon Express
- OIA Global
- PGS
- Rhenus Group
- Röhlig
- Sankyu
- Sanyo Logistics
- Scan Global Logistics
- Seino Schenker
- SEKO Logistics
- Shibusawa Logistics Corporation
- Shin-Ei gumi
- Shiproad
- Sumitomo Warehouse
- UPS
- UPS Supply Chain Solutions
- Yamato Transport
...and many other logistics providers in Japan and around the world.
Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
Recommended Content

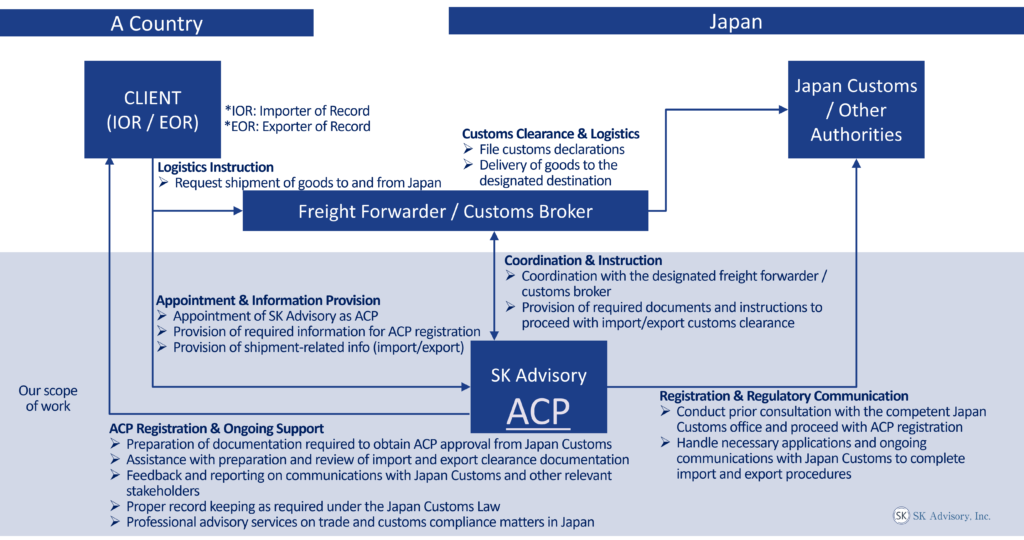
Our ACP Service: The Best Solution for the Japan Importer of Record (IOR) and Exporter of Record (EOR)
ACP is an effective solution for addressing Importer of Record (IOR) and Exporter of Record (EOR) requirements in Japan. Through our ACP service, non-resident entities located outside Japan are able to import and export goods as Non-Resident IOR and EOR.
Below is an overview of our basic scope of work, together with a diagram illustrating the operational structure of the ACP service. Once ACP registration is completed, the non-resident entity can act as the Importer of Record (IOR) and Exporter of Record (EOR) in Japan.
Scope of Work – How We Can Assist
- Consultation with Japan Customs to support successful ACP registration.
- Liaison with relevant stakeholders, including freight forwarders and Japan Customs, to ensure the smooth and compliant import and export of goods.
- Assistance in preparing and reviewing import and export clearance documentation.
- Support in the calculation of customs value, in accordance with the Japan Customs Tariff Act.
- Assistance with advance rulings on HS classification, customs valuation, and rules of origin.
- Import compliance support for regulated products, including Domestic Administrator (sometimes referred to as “Domestic Representative”) Services under the Product Safety Acts (PSE/PSC) and food-related products regulated under the Food Sanitation Act.
- Support for security export control, including list-based classification, catch-all control assessment, and assistance with export license applications to the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI).
- Record-keeping support in accordance with Article 95 of the Japan Customs Law.
- Provision of professional trade and customs advisory services to address and resolve issues that may arise during import or export operations.
**Both import and export activities can benefit from the use of an ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedures). This support is applicable in scenarios where a non-resident acts as the Importer of Record (IOR) for imports and as the Exporter of Record (EOR) for exports.
Three Steps to Initiate Shipments Under the ACP Program:
Quotation Review to Contract Conclusion: Upon receiving your contact details, we will promptly provide a quotation for your review.
Commencing the Registration of ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedures) to Japan Customs: This process is generally completed in about two weeks.
Initiation of First Shipment, Import/Export
Our Japan Consumption Tax (JCT) Representative Services
At SK Advisory Inc., we provide a comprehensive one-stop service that covers both customs procedures through the Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP) and Japan Consumption Tax (JCT) procedures with the National Tax Agency through a designated JCT Tax Representative.
By working closely with our trusted partner tax accountants, we act as your ACP while maintaining close coordination and information sharing with the tax representative. This collaboration ensures the proper deduction and refund of Japan Consumption Tax paid at the time of importation.
Recommended Content

Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
FAQ for ACP (Attorney for Customs Procedures)
What is the role of ACP (SK Advisory)?
- Representation: ACP (SK Advisory) represents the foreign importer and liaises with Japan Customs and the Forwarding Company/Customs Broker.
- Documentation and Compliance: ACP assists in preparing essential import documents (e.g., Invoices) in compliance with Japan Customs Law and formally requests the Customs Broker to proceed with customs clearance.
- Expert Consultation and Troubleshooting: We are a team of legal experts in Customs Laws, providing direct consultations with Japan Customs to ensure compliance and address issues, including troubleshooting unique challenges in non-resident imports.
How long does it take to obtain ACP registration?
It will take approximately 2 weeks until getting an approval from Japan Customs Office.
The breakdown of the task is as follows.
- Prepare the necessary documentation between us
- Start pre-consultation with Japan Customs Office and proceed initial review
- Submit paper-based set of application documents to Japan Customs Office for final review
What documents are required for an ACP application?
Not limited, but for instance - Power of Attorney, Company Registry, The calculation method of Customs Valuation, Catalog of the import goods, business/logistic flow
Can ACP handle all kinds of goods?
While many ACP service providers do not handle the regulated items, our ability to handle those regulated items has become a competitive advantage of our company. We can support the regulated items including cosmetics, PSE-regulated products, foodstuffs, and tableware.
Which regions in Japan are we covering?
Any region in Japan, we can handle.
What is difference between ACP and IOR?
ACP is not the Importer. ACP enables non-resident entities to become IOR (Importer of Record).
Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
Recommended Content

Japan Qualified Invoice System and Compliance JCT (Japan Consumption Tax)
Recently, many companies have been registering as Qualified Invoice Issuers for Japanese Consumption Tax (JCT) due to the new invoice system introduced in October 2023. This new system is similar to the EU's VAT invoice system.
After October 2023, your Japanese customer can’t claim input JCT tax credits unless the sellers(suppliers) issue a qualified invoice that includes a JCT registration number. To issue a qualified invoice, sellers(suppliers) need to be a taxable entity and get a JCT number.
Before October 2023:
Any customer (Company-B) who paid for goods or services could deduct input JCT regardless of whether the seller (Company-A) was registered for JCT. There was no requirement to verify the tax status of the seller.
After October 2023:
Any customer (Company-B) can only deduct input JCT if Company-A, the seller, is registered and can provide a qualified invoice with a JCT registration number. If Company-A cannot issue such an invoice, Company-B may choose not to continue purchases from them.
If Company-A sells only to consumers and not businesses, it may not need to issue qualified invoices since consumers typically do not claim JCT tax returns.

Once Company-A obtains a JCT invoice registration number, it becomes a taxable entity required to file JCT returns regularly.
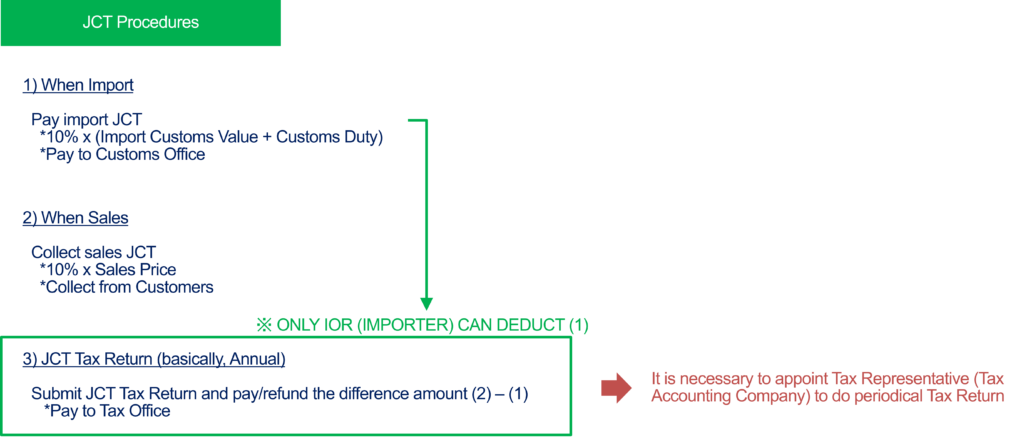
For non-resident entities (Company-A) importing and selling in Japan, the standard procedure involves three steps:
- Pay import JCT to customs: 10% of the import customs value.
- Collect JCT from customers in Japan: 10% of the sales price.
- File a JCT tax return and pay the net JCT to the tax office.
If Company-A paid the import JCT as the importer using an Attorney for Customs Procedures (ACP), they need only pay the net amount of sales JCT minus import JCT.
If Company-A paid the import JCT but was not the importer, they must pay all the collected sales JCT without deducting the import JCT.
Therefore, using an ACP to act as the Importer of Record (IOR) is crucial for managing JCT deductions and refunds. If another company acts as the IOR, you cannot deduct the import JCT, resulting in significant costs.
We strongly recommend using our ACP services to ensure you can act as IOR, optimizing your JCT handling. Our team has extensive experience helping clients become importers and successfully manage their JCT responsibilities. You can rely on our expertise to navigate these complexities.
Contact
Contact us 24 hours through the form
Recommended Content



